Bolt
Your Trustful Fastener Bolt Manufacturer
Fixicore is one of Hex Bolt manufacturers in China since 1986. As a leading & professional China-based Hex Bolt factory, our company manufacturing Many kinds of bolts, Such as Hex Cap Bolt, Hex Flange Bolt,U Bolt, Eye Bolt, set screw, Socket cap screw and with different materials; and also customized products, Contact us today to request a free quote or more information.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
All You Need to Know About Hex Bolts
What does hex mean in bolt?
In the realm of fasteners, the term “hex” is frequently used, especially when referring to bolts. The word “hex” is derived from the Greek word for six and in the context of bolts, it refers to the hexagonal shape of the bolt head.
A hex bolt has a head with six sides and is one of the most common types of bolt heads. This design is particularly practical because it provides multiple surfaces for a wrench to grip, allowing for better torque as compared to a square or rounded head. With six points of contact, hex bolts can efficiently distribute the clamping force and can be securely fastened or loosened.
Hex bolts are extensively used in construction, machinery, and automotive applications among others. The hexagonal shape not only provides the functional benefits of easy tightening and loosening but also ensures that the bolt can withstand the stress and strain of heavy loads without slipping.
In summary, when you come across the term “hex” in relation to bolts, it signifies the six-sided, hexagonal shape of the bolt head, which is an essential design feature for providing better torque and a secure fit in various applications.
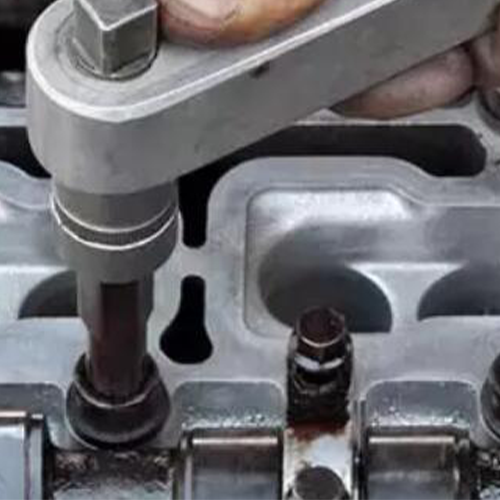


What Hex Bolts Used For?
Set screws, with their unique design, are used to secure an object within another, providing a secure and reliable fastening solution in a wide range of applications.
One of the most common uses for set screws is in the assembly of machinery, where they are used to secure gears, pulleys, or other components onto a shaft. The set screw is threaded into a hole in the component and tightened against the shaft. This effectively locks the component in place, preventing it from moving along the shaft or rotating independently of it.
Set screws are also used in manufacturing equipment, precision instruments, and electronic devices. Their small size and the fact they don’t protrude from the surface make them ideal for applications where space is limited or where a smooth, flush finish is desired.
In addition to these industrial applications, set screws find use in everyday items. For instance, they are often used in door handles and knobs to secure the handle to the spindle.
Despite their simplicity, set screws play a crucial role in the functionality and efficiency of numerous mechanical systems, serving as an indispensable fastening solution in a multitude of applications.
Types of Hex Bolts
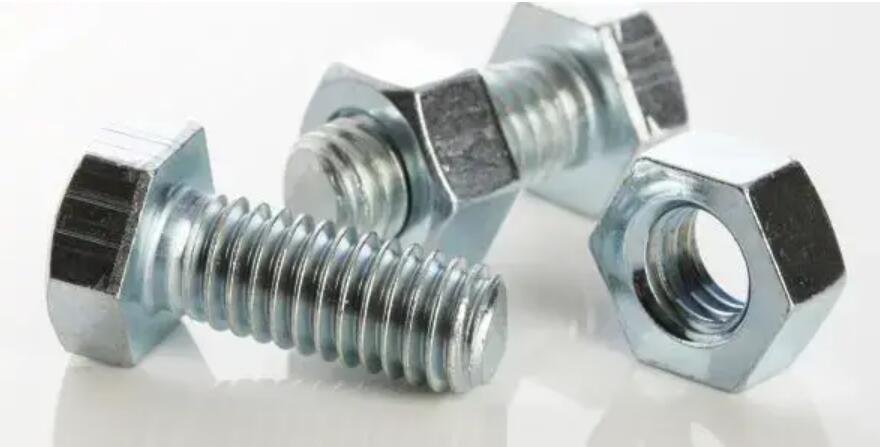

Bolts are one of the most commonly used mechanical fasteners in engineering. Bolts are used to connect two or more objects together, either permanently or temporarily. There are different types of bolts used in engineering, each designed for specific purposes.
Hex bolts, identifiable by their six-sided heads, are indispensable in various industries and applications. The hexagonal shape provides multiple gripping points, making them ideal for situations that require a tight and secure connection. Here, we delve into the different types of hex bolts and their specific uses.
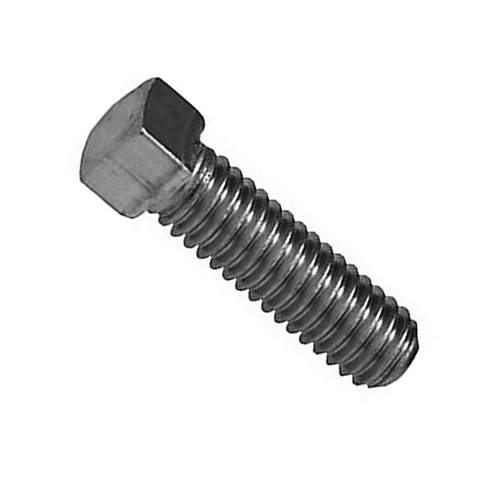
Hex Cap Bolt
Hex cap bolt closely resemble hex bolts but have a tighter tolerance on the threads. They are primarily used in precise applications where the mating threads are already in place. Hex cap screws are popular in machinery, automotive manufacturing, and construction for fastening metal parts.
Carriage Bolts
Carriage bolts have a rounded head with a square section underneath. This design ensures that the bolt remains in place when the nut is tightened. Carriage bolts are often used in wood applications, including furniture and wooden structures, where a smooth finish is required.
Hex Tap Bolts
Hex tap bolts are fully threaded hex bolts. The extended threading makes them suitable for applications where a nut can't be used on the opposite side. They are commonly employed in housing and mounting brackets, where the bolt threads directly into the receiving material.
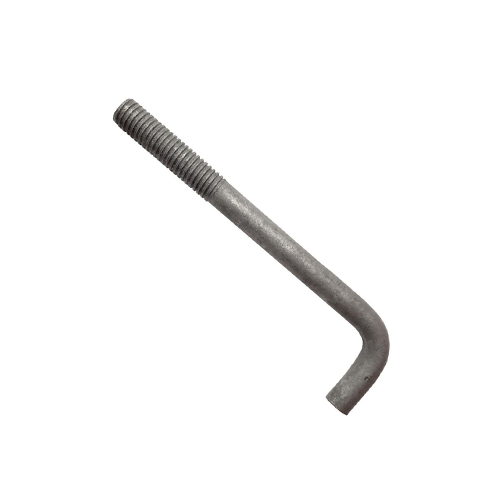
J-Bolts
J-Bolts have a J-shaped design, with threading on the longer end. They are often used for hanging electrical cables and plumbing pipes, as well as in structural applications where an anchor is embedded in concrete.
Flange Bolts
Flange bolts have an integrated flange on the bottom of the head, which eliminates the need for a washer. The flange helps distribute the load across a broader surface area. These bolts are frequently used in automotive applications and pipe fittings, where a secure, tight connection is essential.
Eye Bolts
Eye bolts feature a looped head and are used for attaching cables, ropes, or chains. They are commonly used in applications where items need to be hung, lifted, or tethered.
Structural Bolts
Structural hex bolts are designed for heavy-duty applications, particularly in the construction industry for joining structural steel. They have a larger, thicker head compared to standard hex bolts, which ensures that they can withstand the high levels of tension and pressure in structural applications.
U-Bolts:
U-Bolts have a U-shaped design and are used to attach pipes or tubes to surfaces. They are common in vehicle suspension systems and plumbing applications.
Heavy Hex Bolts:
As the name suggests, heavy hex bolts have a larger head compared to standard hex bolts. This design allows them to withstand higher levels of stress and tension. Heavy hex bolts are commonly used in industrial applications, such as bridge construction, where structural integrity is paramount.
Timber Bolts:
Timber bolts, also known as economy bolts or mushroom head bolts, have a rounded, low-profile head and are used in wood applications, specifically in wooden docks and bridges. The underside of the head features fins which prevent the bolt from turning when the nut is tightened.
Hex bolts, with their distinctive six-sided heads, come in a plethora of types, each serving a particular purpose. From hex cap screws for precise fastening to heavy hex bolts for structural integrity, the varied designs and functionalities of hex bolts make them an essential component in countless applications across industries. Understanding the specific types and their uses can help in making informed decisions in your projects.
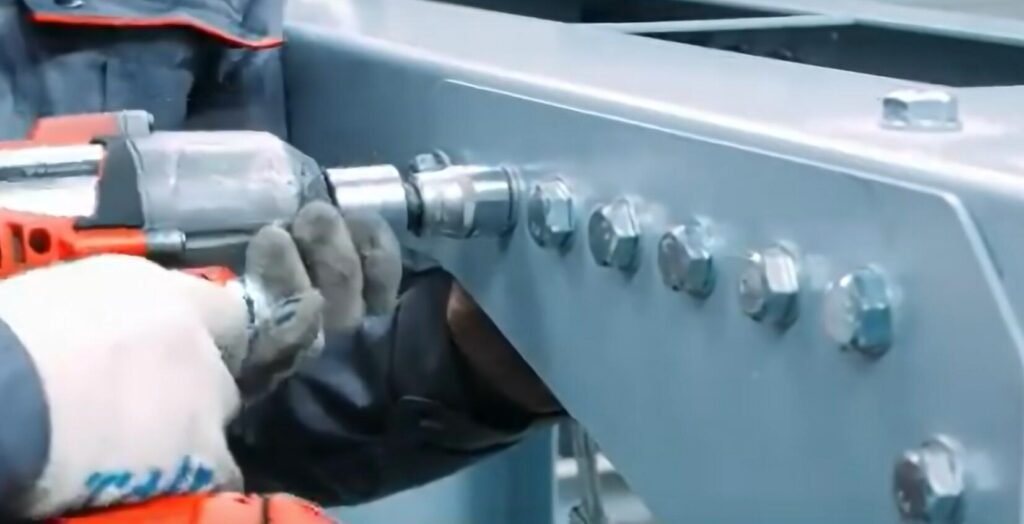

How Do Hex Bolt Work?
Hex bolts, renowned for their six-sided heads, serve as robust fasteners. To use a hex bolt, you align the parts to be joined and insert the bolt through the holes. A nut is then threaded onto the bolt. Using a wrench or socket, you apply torque to the hexagonal head of the bolt or the nut. This action causes the threads on the bolt and nut to interlock, pulling the bolt upwards and pressing the materials together. The hexagonal head ensures multiple contact points for the tool, allowing for secure tightening. This simple mechanism creates strong, stable connections in construction, machinery, and more.
Expanding Horizons: The Multifaceted Applications of Hex Bolts
Hex bolts, distinguished by their six-sided heads, are fundamental components in an array of applications across industries. The versatility and strength of hex bolts make them an invaluable asset. In this article, we will delve into various applications where hex bolts play a pivotal role.
1. Construction and Infrastructure:
In construction, hex bolts are vital for securing beams, timber, and other structural elements. From bridges and highways to buildings and homes, hex bolts ensure the structural integrity of various edifices. Heavy hex bolts, in particular, are used for applications where high strength is necessary due to their larger and thicker head compared to standard hex bolts.
2. Automotive and Transportation:
Hex bolts find extensive use in the automotive industry. From engine assembly to securing components in the vehicle’s chassis, they are indispensable for the assembly and maintenance of vehicles. They are also used in the manufacturing of aircraft, ships, and railways.
3. Machinery and Equipment:
In machinery, hex bolts are essential for holding together various components. They are used in agricultural machinery, factory equipment, and even in smaller appliances. Hex bolts in machines need to withstand vibration and stresses, and as such, are often chosen for their strength and reliability.
4. Renewable Energy:
With the surge in renewable energy sources, hex bolts have found new avenues. In wind turbines, hex bolts are used to assemble the nacelle, secure the blades, and fasten the tower sections. The structural stability of these gigantic structures is ensured through the use of heavy-duty hex bolts.
5. Electronics and Computer Industry:
While hex bolts used in electronics are typically smaller, they are no less important. They are used in assembling server racks, mounting hardware, and securing components in place. In computers, hex bolts can often be found securing the power supply and attaching the motherboard to the casing.
6. Outdoor and Garden Structures:
Hex bolts are commonly used in outdoor structures such as fences, decks, and pergolas. They are favored for their strength and the ease with which they can be tightened or loosened. Galvanized or stainless steel hex bolts are often chosen for these applications for their resistance to weather and corrosion.
7. Furniture Assembly:
In furniture making, hex bolts are used to fasten legs to tables, attach sections of shelving units, and secure other components. They provide both strength and ease of assembly or disassembly, which is particularly useful in flat-pack furniture.
8. Custom Fabrication and DIY Projects:
For hobbyists and those engaged in custom fabrication, hex bolts are a go-to fastener due to their reliability and the simplicity with which they can be used. They are employed in building custom vehicles, creating artwork, and numerous other DIY projects.
Conclusion:
Hex bolts, with their signature hexagonal heads, are the backbone of countless applications. Their strength, coupled with the ease of installation, makes them a favorite across diverse industries. From the towering wind turbines to the intricate electronics, hex bolts continue to be an irreplaceable component in bridging gaps and holding the world together.
Decoding the Bolt Grade: A Guide to Identification
Bolt grades are crucial indicators of the strength and material of a bolt, ensuring its suitability for specific applications. Knowing how to identify the grade of a bolt is essential for maintaining structural integrity and safety. Here is a brief guide to help you decode bolt grades.
1. Look for Head Markings:
One of the most common ways to identify the grade of a bolt is by inspecting the markings on its head. For instance, SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) graded bolts usually have radial lines. A Grade 2 bolt has no markings, a Grade 5 has three lines, while a Grade 8 has six lines. Metric bolts use numbers such as 8.8 or 10.9, where the first number represents the tensile strength, and the number after the decimal point indicates the yield strength ratio.
2. Material and Manufacturing Standards:
Sometimes the bolt head also contains letters or abbreviations representing the material, such as ‘SS’ for stainless steel. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards might also be stamped, indicating the bolt adheres to specific material and manufacturing requirements.
3. Thread Pitch and Diameter:
While not a direct indication of grade, knowing the thread pitch and diameter can sometimes help you deduce the likely grade of the bolt. Coarse threads are standard for lower grade bolts, whereas fine threads are often found in higher-grade bolts.

4. Manufacturer’s Mark:
Often, the manufacturer’s mark is also present. Knowing the manufacturer can allow you to reference their documentation or website for further information on the bolt grade.
5. Corrosion Resistance:
Sometimes the appearance of the bolt can give you a clue about its grade. For example, a shiny, non-magnetic bolt is likely made of stainless steel and would be a high-grade bolt.
6. Seek Expert Advice:
When in doubt, it’s always best to consult the manufacturer or an expert in fasteners. They can provide information not just on the grade but also on the most suitable bolts for your specific application.
In conclusion, being able to identify the grade of a bolt is paramount in ensuring that the fasteners used are capable of withstanding the pressures and stresses of their intended application. Always double-check for markings and consult experts if unsure. The grade is not just a number; it’s an assurance of quality, strength, and reliability.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Hex Cap Bolt Buyer's Guide: Know Your Grade
When it comes to purchasing hex cap screws for any project, knowing the grade of the screw is paramount. The grade indicates the screw’s strength and material properties, which are vital in ensuring the safety and integrity of your application. This buyer’s guide will steer you through the essential considerations when selecting the appropriate grade for hex cap screws.

1. Look for Head Markings:
One of the most common ways to identify the grade of a bolt is by inspecting the markings on its head. For instance, SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) graded bolts usually have radial lines. A Grade 2 bolt has no markings, a Grade 5 has three lines, while a Grade 8 has six lines. Metric bolts use numbers such as 8.8 or 10.9, where the first number represents the tensile strength, and the number after the decimal point indicates the yield strength ratio.
2. Material and Manufacturing Standards:
Sometimes the bolt head also contains letters or abbreviations representing the material, such as ‘SS’ for stainless steel. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards might also be stamped, indicating the bolt adheres to specific material and manufacturing requirements.
3. Check for Head Markings:
Hex cap screws usually have markings on the head that indicate their grade. For example, Grade 5 screws typically have three radial lines, while Grade 8 screws have six. Metric screws may have numbers stamped on them, like 8.8 or 10.9.
4. Consider Material and Corrosion Resistance:
The material of the screw is also a part of its grade. Stainless steel hex cap screws are often chosen for their corrosion resistance, which is crucial in environments like marine applications. If corrosion resistance is a priority, look for stainless steel or screws with special coatings such as zinc or galvanized.
5. Seek Expert Advice:
If you are unsure which grade to choose, don’t hesitate to seek advice from fastener specialists or manufacturers. They can provide insights into the best options for your specific application.
6. Verify Manufacturer’s Compliance:
Ensure that the manufacturer complies with standards like ASTM or ISO. This compliance is a testament to the quality and reliability of the screws.
Request A Free Quote
We'd like to work with you
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. Our experts will give you a reply within 24 hours and help you select the right valve you want.
- +86 577 5768 9696
- Info@fixicore.com