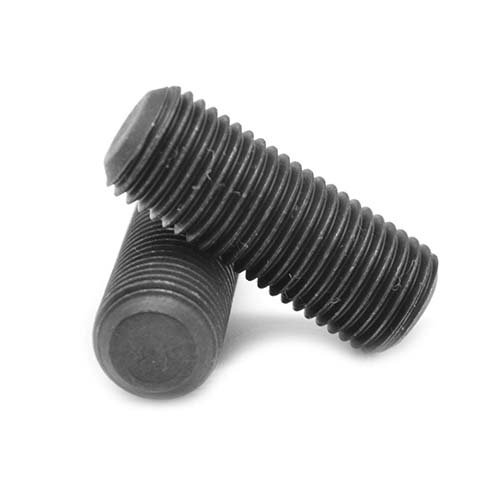
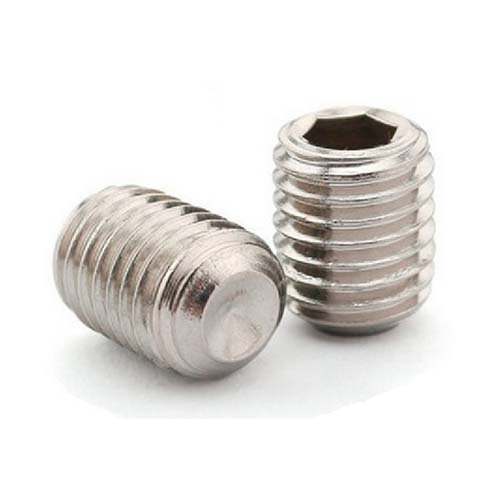
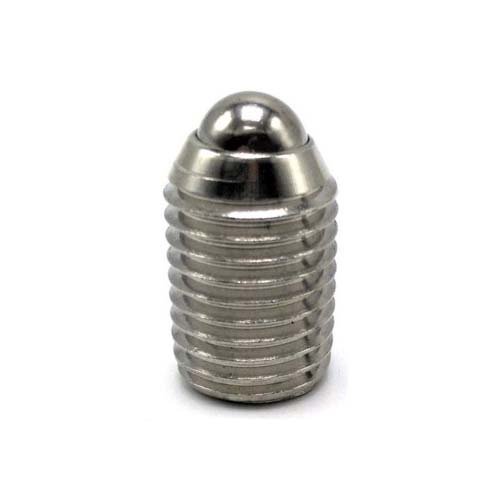
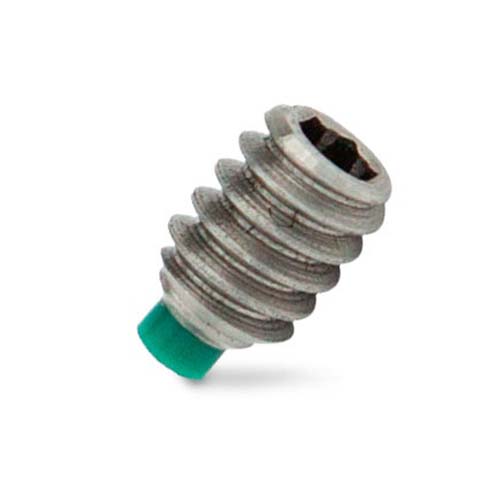
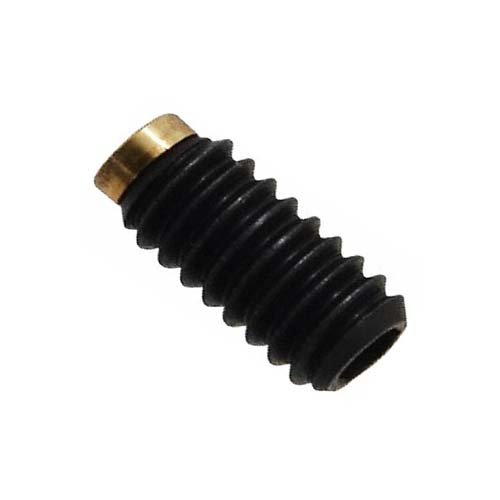
Socket Set Screw
Your Trustful Set Screw Supplier
Fixicore is one of Socket Set Screw manufacturers in China since 1986. As a leading & professional China-based Socket Screw factory, our company manufacturing Many kinds of Socket Screws, Such as set screw, Socket cap screw and with different materials; and also customized products, Contact us today to request a free quote or more information.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
All You Need to Know About Socket Set Screw
What is a Set Screw?
A set screw is a type of fastener that’s typically used to secure one object within another. Unlike traditional screws, which have a head and are designed to clamp components together by distributing the screw’s load across the surface, set screws are headless and fully threaded. They exert their clamping force directly through the tip that bears on the component.
Set screws are driven into a threaded hole in the inner object until they press firmly against the outer object. They’re often used to secure pulleys or couplings onto shafts – the set screw locks onto the shaft, either by digging into the surface if the pressure is high enough, or fitting into a small depression or hole.
Set screws are available in a variety of point styles, each serving a different purpose. The most common styles are the cup, cone, flat, dog, and oval points. The choice of point is typically dictated by the hardness and durability of the surface material and whether the connection is permanent or needs to be disassembled and reassembled.
The simplicity of set screws belies their importance in many mechanical applications, where they provide an effective and efficient method of fastening components together.
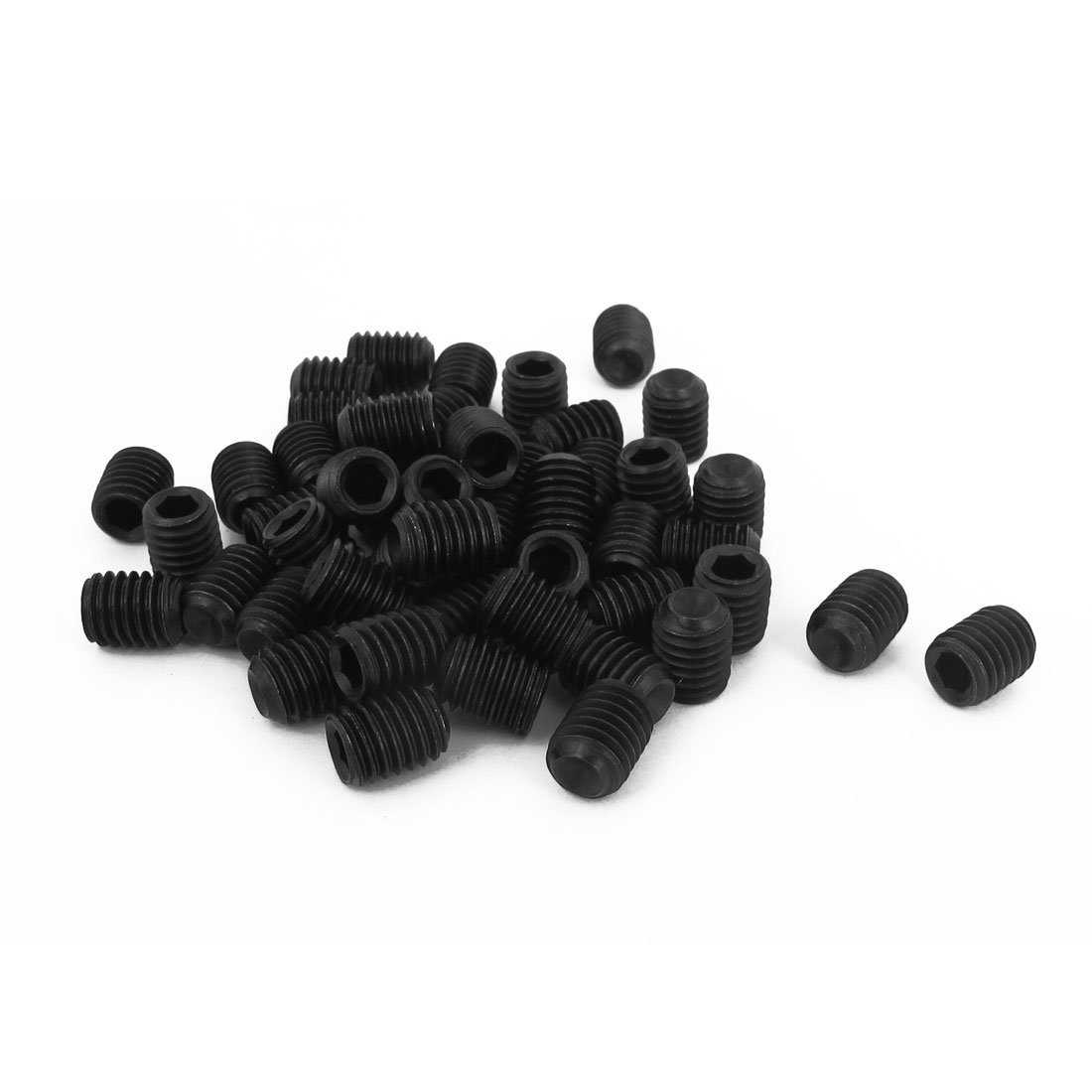


What Are Set Screws Used For?
Set screws, with their unique design, are used to secure an object within another, providing a secure and reliable fastening solution in a wide range of applications.
One of the most common uses for set screws is in the assembly of machinery, where they are used to secure gears, pulleys, or other components onto a shaft. The set screw is threaded into a hole in the component and tightened against the shaft. This effectively locks the component in place, preventing it from moving along the shaft or rotating independently of it.
Set screws are also used in manufacturing equipment, precision instruments, and electronic devices. Their small size and the fact they don’t protrude from the surface make them ideal for applications where space is limited or where a smooth, flush finish is desired.
In addition to these industrial applications, set screws find use in everyday items. For instance, they are often used in door handles and knobs to secure the handle to the spindle.
Despite their simplicity, set screws play a crucial role in the functionality and efficiency of numerous mechanical systems, serving as an indispensable fastening solution in a multitude of applications.
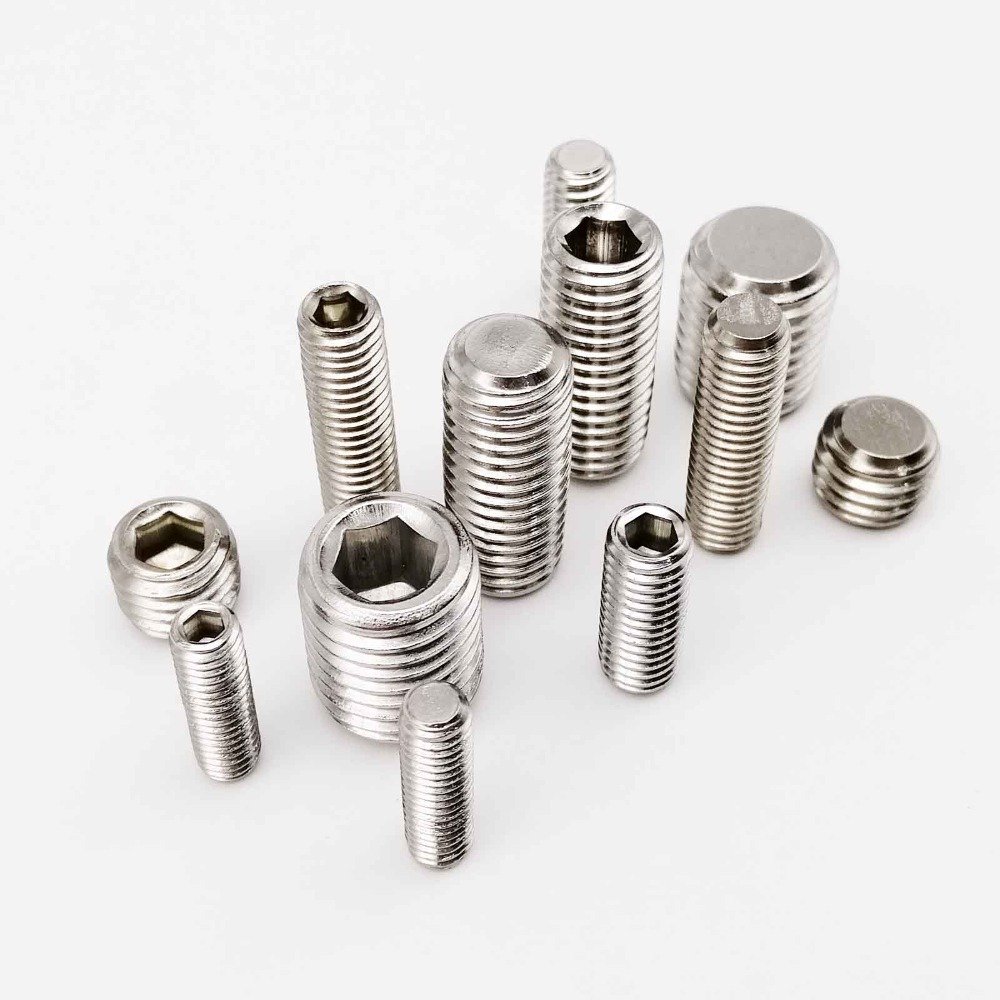
Types of Set Screw
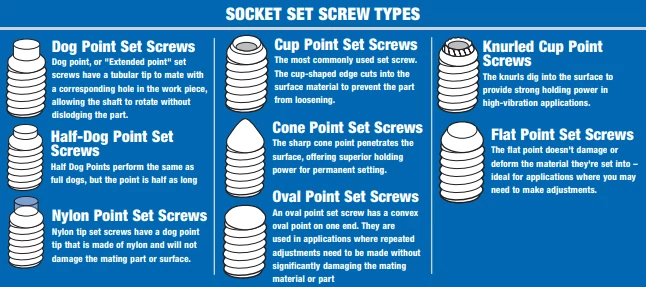
Set screws are a fundamental component in many mechanical applications, utilized for securing an object within another by exerting clamping force. With various point styles available, each serves a specific purpose and is chosen based on application requirements. This article offers a comprehensive overview of the different types of set screws and their respective functions.
Flat Point Set Screws
Flat point set screws have a flat surface on the bottom. They are typically used for securing objects that need to be perfectly aligned or require more surface contact with the point. The flat point causes minimal damage to the surface it is secured against.
Oval Point Set Screws
Oval point set screws have a rounded point that is less likely to cause surface damage compared to other types. They are often used for applications where frequent adjustments are necessary or where the set screw needs to be easily removed without causing damage.
Cone Point Set Screws
The cone point set screw has a sharp, conical point that embeds itself into the part it is tightened against. This type is used for permanent or semi-permanent installations, particularly where frequent reassembly is not required. The pointed end allows for easier penetration and a tighter grip.
Knurled Cup Point Set Screws
Knurled cup point set screws have a serrated edge on the cup, which allows for better locking grip. They are used in applications where vibration is common, as the serrations resist loosening. These are suitable for use in applications where a strong grip is required without excessively marring the surface.
Dog Point Set Screws
The dog point set screw has an extended flat tip. It is used to permanently set parts, and the flat tip provides more contact with the shaft. This type is commonly used in applications where the set screw replaces a dowel pin for fastening.
Slotted Set Screws
Slotted set screws are small, headless fasteners used to secure an object within or against another object. The primary feature that distinguishes them is the straight slot on one end, which accommodates a flat-head screwdriver for installation. slotted set screws are valued for their simplicity and effectiveness in providing a secure fit without the bulk of a traditional screw head.
Cup Point Set Screws
Cup point set screws are the most common type. They feature a cup-shaped point which provides a strong grip with minimal surface damage. Their holding action is powerful, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, including securing pulleys and gears to shafts.
Nylon Tip Set Screws:
These set screws have a soft nylon tip, which minimizes damage to the part it is securing. They are used in applications where surface protection is important, such as with painted or finished surfaces.
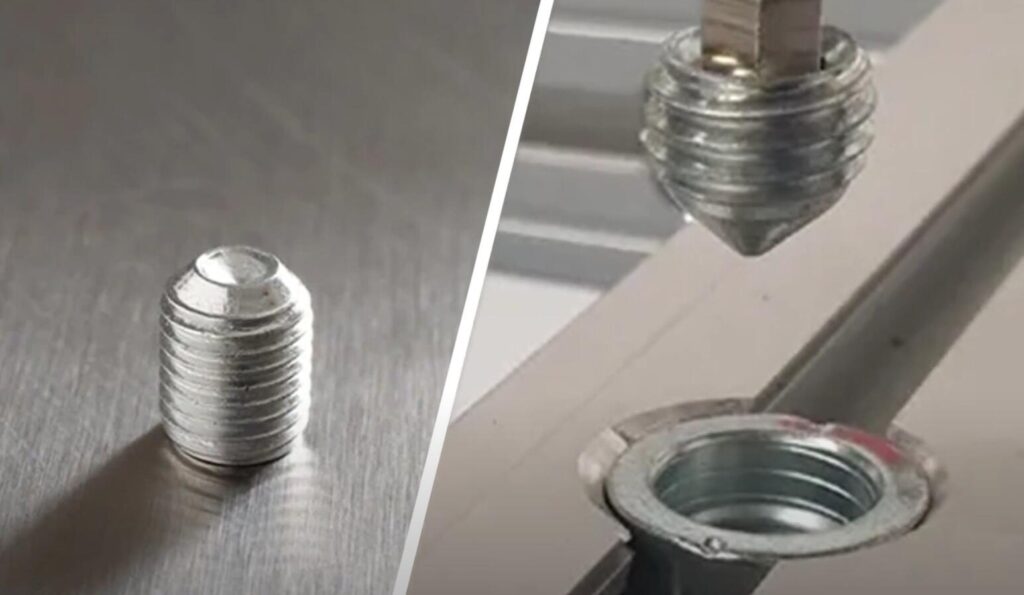

How Do Set Screws Work?
Set screws are specialized fasteners that play an integral role in holding objects in position, particularly within machinery and mechanical assemblies. Unlike conventional screws with heads, set screws are headless and exert clamping force at the tip to prevent relative motion between objects. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of how set screws work and explore their applications.
Application for Set Screw
Mechanism of Action:
Set screws are usually threaded into a pre-drilled hole in the inner object until they press firmly against the outer object, thus securing the two objects together. The clamping action is the result of the set screw’s tip applying pressure onto the outer surface. This pressure can either create a small indentation in the outer object for a more secure grip or it can press against a flat surface for easy adjustments and removal.
Types of Tips:
The functioning of set screws is greatly influenced by the type of tip they possess. For example, a cup point set screw has a concave tip that is designed to deform the surface material slightly, providing a strong grip. Conversely, a flat point set screw has a flat tip which makes surface contact, allowing for easy repositioning with minimal surface damage. Each tip type serves a specific purpose and is chosen based on application requirements.
Torque:
The effectiveness of a set screw also depends on the amount of torque applied during installation. Insufficient torque can lead to the screw loosening under vibration, while excessive torque can cause damage to the components or strip the threads. It’s vital to apply the appropriate amount of torque to ensure that the set screw functions as intended.
Materials and Coatings:
Set screws can be made from various materials like stainless steel, alloy steel, or brass, and sometimes have coatings like zinc or black oxide for increased corrosion resistance. The choice of material and coating can affect the set screw’s performance, particularly in harsh environments.
Applications:
Machinery & Mechanical Devices: Set screws are extensively used in machinery to secure gears, pulleys, and other components to shafts. They ensure that the components do not move independently of the shafts, which is essential for the machinery to function properly.
Handles and Knobs: Set screws are often found in door handles and knobs, where they are used to secure the handle or knob to a spindle. This allows the handle or knob to turn the spindle without slipping.
Precision Equipment: In precision equipment such as lab instruments, set screws can be used to make fine adjustments or calibrations by holding certain components in place.
Fixture & Mounting: Set screws are employed in fixtures and mounting applications to secure objects such as shelves, brackets, or other hardware.
In conclusion, set screws work by applying pressure through their tip to an outer object to prevent it from moving relative to an inner object. They are an essential component in many applications, especially in machinery where they ensure the secure and proper functioning of components. The selection of the appropriate tip type, material, and torque is vital to the set screw’s effectiveness and longevity.
What is the Difference Between Set Screw and Screw?
Screws are among the most common and versatile fasteners used in a variety of applications, ranging from construction to electronics. Among screws, a special category known as set screws is designed for particular applications. Although they share similarities as fasteners, there are distinctive differences between set screws and standard screws. In this article, we will explore these differences in detail.
Design and Structure
One of the most apparent differences between set screws and standard screws is their physical design. Standard screws typically have a head which allows them to be driven into materials with the help of a screwdriver or drill. The head also serves as a stop, preventing the screw from going further into the material than necessary.
Set screws, on the other hand, are headless. They are designed to be fully threaded and are usually installed into a pre-tapped hole, exerting pressure on an opposite component.
Purpose and Application
Standard screws are primarily used to hold materials together. They can be used in wood, metal, plastic, and various other materials. The threaded part of the screw digs into the material, creating a grip that holds the pieces together.
Set screws have a different purpose. They are used to secure one object inside another. Instead of holding materials together through the threads, set screws exert a clamping force at the tip to prevent relative motion between the objects. For example, a set screw might be used to hold a gear or pulley in place on a shaft.
Point Styles
Set screws come in different point styles such as cup, cone, flat, and dog point, among others. These point styles serve specific functions, like resisting vibration, causing minimal damage to the surface, or providing high holding power.
In contrast, standard screws usually have a pointed or flat end but do not exhibit the variety of point styles seen in set screws. The focus in standard screws is more on the type of head, which could be flat, round, pan, truss, or hex, among others.
Torque and Pressure
Set screws are generally tightened with a higher torque compared to standard screws. This is because they need to exert sufficient pressure on the mating component to prevent any slippage. Standard screws usually don’t need as much torque because their primary function is to hold materials together.
Removal and Adjustments
Standard screws with heads are easier to remove or adjust, as the head provides a grip for the screwdriver or drill. Set screws, being headless, are less likely to be removed or adjusted frequently. In cases where set screws need to be adjusted, an Allen wrench is usually used.
Material Interaction
Set screws often interact with the surface they press against, sometimes deforming it for a secure grip. Standard screws mainly rely on the threads to interact with the material they are driven into.
While both set screws and standard screws are essential fasteners in the engineering and construction world, they serve different purposes and have distinct features. Set screws are headless and are used to fasten an object inside another by exerting pressure. Standard screws have a head and are used for holding materials together. The selection between a set screw and a standard screw depends on the specific application and requirements at hand.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
What is the difference between a grub screw and a set screw?
In the world of fasteners, terminology can sometimes be confusing. This is especially true when it comes to differentiating between similar components such as grub screws and set screws. Many people use these terms interchangeably, and indeed, there’s a good reason for that. In this article, we will clarify the terminology and explore whether there is any distinction between grub screws and set screws.

Grub Screw and Set Screw: A Common Identity
Grub screws and set screws essentially refer to the same type of fastener. Both terms are used to describe a small, headless screw that is used to secure one object within another. These screws do not have a head like conventional screws. Instead, they are threaded over their entire length and are tightened using an internal driving design, such as a hexagonal socket.
The term "grub screw" is more commonly used in British English, while "set screw" tends to be the preferred term in American English. However, the terminology can vary in different regions and industries.
Request A Free Quote
We'd like to work with you
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. Our experts will give you a reply within 24 hours and help you select the right valve you want.
- +86 577 5768 9696
- Info@fixicore.com